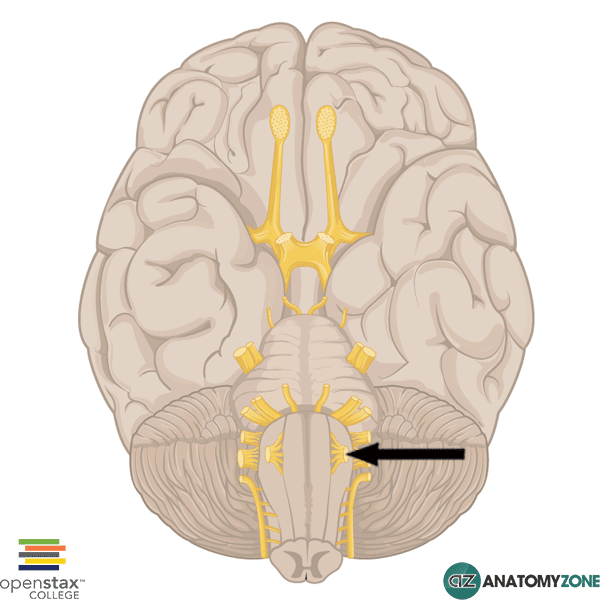
Hypoglossal Nerve
The structure indicated is the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII).
The hypoglossal nerve carries general somatic efferent nerve fibres and is responsible for motor innervation to the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue. It arises from the hypoglossal nucleus located in the caudal brain stem and emerges from the preolivary sulcus in the ventromedial aspect of the medulla oblongata from several rootlets. The preolivary sulcus separates the olive from the medullary pyramids. The hypoglossal nerve then passes through the subarachnoid space and exits the skull through the hypoglossal canal.
The extrinsic muscles of the tongue are as follows:
- Genioglossus
- Hyoglossus
- Styloglossus
- Palatoglossus
Damage to the hypoglossal nerve causes weakness of the tongue muscles resulting in deviation of the tongue towards the side of the lesion.
Learn all about the cranial nerves in this anatomy tutorial.
Learn all about the extrinsic muscles of the tongue in this anatomy tutorial.